 Dopamine is a chemical messenger that plays a vital role in transmitting signals between nerve cells in the brain. It is often referred to as a “feel-good” neurotransmitter because it contributes to feelings of pleasure and satisfaction. However, dopamine’s role extends beyond just making people feel good. It is involved in several vital processes, including maintaining mental health, memory, and motivation. When the brain releases dopamine, it can affect emotions, behavior, and even physical movements. Keeping dopamine levels in balance is essential for overall well-being because of its broad impact on the body’s functions.
Dopamine is a chemical messenger that plays a vital role in transmitting signals between nerve cells in the brain. It is often referred to as a “feel-good” neurotransmitter because it contributes to feelings of pleasure and satisfaction. However, dopamine’s role extends beyond just making people feel good. It is involved in several vital processes, including maintaining mental health, memory, and motivation. When the brain releases dopamine, it can affect emotions, behavior, and even physical movements. Keeping dopamine levels in balance is essential for overall well-being because of its broad impact on the body’s functions.
Where Does the Body Get Dopamine From?
The body does not store dopamine in large quantities. Instead, it produces it on demand. Dopamine is synthesized from an amino acid called tyrosine, which is found in various foods, particularly those that are high in magnesium and precursor molecules to tyrosine, such as phenylalanine. Examples of such foods include green leafy vegetables and green tea, both of which help the body boost dopamine production.
Through a complex series of reactions triggered by enzymes, the body converts tyrosine into dopamine. Two key steps are involved in converting tyrosine into dopamine. These processes primarily occur in the brain, but dopamine can also be synthesized in smaller quantities in other parts of the body.
Factors like diet and lifestyle can significantly influence the body’s ability to produce dopamine. For instance, engaging in activities that provide pleasure or satisfaction, such as eating, exercising, or listening to music, can temporarily increase dopamine levels.
How Does the Body Use Dopamine?
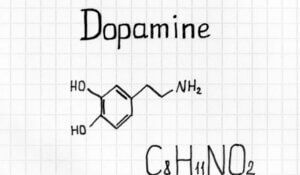
Another way of understanding how dopamine works has come from Prof. Daniel Lieberman, clinical professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at George Washington University. He sets out an alternate theory in his book “The Molecule of More.” In this alternative picture, dopamine fuels people’s desires rather than being the “reward” molecule released when a pleasurable activity has finished. This explains why people set out to find new stimuli, acting as the chemical driving force behind the pursuit of goals.
Dopamine is also crucial for coordinating smooth and controlled physical movements. It helps relay signals from the brain to the muscles, making voluntary movement possible. This is why a condition like Parkinson’s disease, which is characterized by a dopamine deficiency, results in difficulty controlling movement.
Dopamine also plays a critical role in cognitive functions such as attention, learning, and memory. It modulates motivation, influencing how people pursue their tasks and goals. For example, low dopamine levels are associated with decreased motivation and lethargy, while balanced levels make individuals more focused and driven to achieve their goals.
Dopamine’s role is not confined to these functions. It also affects sleep cycles, mood, and decision-making. In other words, dopamine is integral to the body’s physical and emotional well-being and ability to interact with the environment.
What Happens When Dopamine Levels Are Abnormal?

Dopamine Deficiency
Low dopamine levels have been linked to various conditions, including Parkinson’s disease and Attention-deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). In ADHD, dopamine’s role in controlling attention and focus appears to be impaired, making it difficult for individuals to maintain concentration. Similarly, in Parkinson’s disease, the loss of dopamine-producing neurons results in distinguishing motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and slow movement.
Depression and other mood disorders can also be related to insufficient dopamine levels. Since dopamine contributes to feelings of pleasure and satisfaction, a dopamine deficiency can lead to a lack of motivation, feelings of helplessness, and even suicidal thoughts. Other symptoms of low dopamine include fatigue, apathy, and a reduced ability to feel joy or pleasure.
Excess Dopamine
Apart from dopamine deficiency, having too much dopamine can lead to its own set of problems. Excess dopamine is linked to mental health conditions such as schizophrenia, where it may contribute to hallucinations and delusions. Some studies also suggest that excessive dopamine activity may lead to manic behavior in individuals with bipolar disorder.
Overactivity in the dopamine system may also be involved in addiction. Substances such as drugs, alcohol, and even caffeine can overstimulate the dopamine system, reinforcing the behaviors that trigger their release. This can lead to dependency because the body craves the constant stimulation of its dopamine pathways.
How Can Dopamine Levels Be Controlled?
Managing dopamine levels is essential for maintaining both physical and mental health. Fortunately, there are several ways to influence dopamine production and ensure it stays balanced.
Diet and Supplements

Certain supplements may also be recommended to boost dopamine levels, particularly in individuals with diagnosed deficiencies. For example, L-DOPA, the first step in the chain of converting tyrosine into dopamine, is often prescribed to Parkinson’s patients to increase dopamine production in the brain directly. However, such treatments should always be undertaken under medical supervision, as improper use can lead to side effects.
Engaging in Activities That Increase Dopamine
Physical activity, meditation, and even passive activities like listening to music can help boost dopamine levels. In particular, exercise is known to trigger the release of dopamine, making it an effective way to elevate mood and reduce stress. Similarly, engaging in enjoyable hobbies or social activities stimulates dopamine production, helping to regulate mood and motivation.
Medical Treatments
In cases where dopamine levels are severely out of balance, medical interventions may be necessary. For example, people with early-stage Parkinson’s disease can benefit from medications that boost L-DOPA levels to help restore lost dopamine. Examples of these include Sinemet and Stalevo,
For patients with mental health conditions such as schizophrenia or ADHD, medications that either block excess dopamine or enhance its activity in specific parts of the brain may be prescribed. Additionally, lifestyle adjustments such as reducing stress, getting adequate sleep, and avoiding substance abuse can play an important role in managing dopamine levels naturally.
Summary

The body produces dopamine primarily from the amino acid tyrosine, found in foods such as green leafy vegetables and green tea. When dopamine levels become abnormal, either too high or too low, medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and dietary adjustments can help restore balance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dopamine
Please remember that dopamine is just one factor in complex conditions like depression and ADHD. Oversimplification should be avoided. You should consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of dopamine-related issues. These FAQs should not be taken as medical advice.
What stimulates dopamine levels?
Dopamine levels can be stimulated by engaging in activities that a person finds enjoyable, such as eating favorite foods, exercising, or spending time with friends and loved ones. Physical activities, listening to music, can also trigger a release of dopamine.
Does caffeine increase dopamine?
Yes, caffeine can increase dopamine levels, but only temporarily. Its basic stimulating effect triggers a release of dopamine, which is why consuming it can make a person feel more alert and focused. However, excess caffeine consumption can lead to tolerance, making it less effective over time.
How to check dopamine levels at home?
It is not currently possible to check dopamine levels directly at home. Measuring dopamine levels requires specific tests that only healthcare professionals can perform, usually involving blood samples or brain imaging.
Is ADHD a dopamine deficiency?
ADHD has been associated with low dopamine levels in the brain, particularly in areas responsible for attention, focus, and motivation. This is why many treatments for ADHD work by increasing dopamine activity in these specific areas in the brain.
What triggers dopamine release?
There is no single theory that fully explains the production of dopamine. One theory holds that dopamine is released in response to pleasurable experiences, such as eating good food, engaging in enjoyable social interactions, or achieving a personal goal. An alternate theory proposes that dopamine drives people’s desires. In both cases, the brain’s reward system is closely linked to dopamine release, reinforcing behaviors that provide satisfaction.
What are the symptoms of low dopamine?
Symptoms of low dopamine include fatigue, low motivation, difficulty concentrating, feelings of apathy, and, in severe cases, depression. Individuals may also struggle with emotional regulation and experience a diminished capacity to feel joy.
What is Dopamine?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, a chemical messenger that carries signals between neurons in the brain. It is often called the “feel-good” neurotransmitter because it is associated with feelings of pleasure and reward. However, dopamine’s functions extend beyond just pleasure; it plays a vital role in motivation, memory, attention, movement, and more.
How does the body produce dopamine?
The body produces dopamine from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyrosine is found in various foods, especially protein-rich foods like meat, dairy, and legumes. It is also found in certain fruits and vegetables, particularly green leafy vegetables and green tea. Tyrosine is converted into dopamine through a series of enzymatic reactions within the body.
What are the symptoms of low dopamine levels?
Low dopamine levels can manifest in various ways, including:
- Dopamine plays a role in regulating energy levels, so that low levels can lead to persistent tiredness, fatigue, and lack of energy.
- It is crucial for motivation and drive, and a deficiency can result in a lack of interest in once-enjoyable activities.
- Dopamine is involved in attention and focus, and low levels can make it challenging to stay on task and cause difficulty concentrating and focusing.
- It influences mood regulation, and a deficiency can lead to increased irritability, emotional instability, and mood swings.
- Low dopamine levels are associated with depression and feelings of hopelessness and sadness.
- Dopamine plays a role in regulating sleep-wake cycles, and a deficiency can disrupt sleep patterns.
What are the health consequences of abnormal dopamine levels?
Both low and high dopamine levels can lead to health problems:
- Conditions associated with low dopamine include Parkinson’s disease, ADHD, depression, and Restless Leg Syndrome.
- While less common, high dopamine levels are linked to conditions like schizophrenia and addiction.
How can I increase my dopamine levels naturally?
There are several lifestyle modifications and natural methods to support healthy dopamine levels:
- Consuming a balanced diet rich in tyrosine-rich foods like lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, nuts, seeds, beans, and lentils can provide the building blocks for dopamine production.
- Regular physical activity (such as aerobic exercise and strength training) has been shown to increase dopamine levels and improve mood.
- Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night to support dopamine production and overall brain health.
- Chronic stress can deplete dopamine levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Participating in hobbies, listening to music, and spending time with loved ones can trigger dopamine release.
What is the relationship between dopamine and addiction?
Addictive substances, such as drugs, alcohol, and nicotine, artificially stimulate the release of dopamine in the brain’s reward pathway, creating a feeling of intense pleasure. This surge in dopamine reinforces the addictive behavior, making it difficult to stop despite negative consequences.
Can dopamine levels be tested?
There is no simple, at-home test to measure dopamine levels. Assessing dopamine levels typically involves specialized medical tests, such as blood tests or brain imaging studies, conducted by healthcare professionals.
What are the treatment options for dopamine deficiency?
Treatment for dopamine deficiency depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. Options may include:
- In conditions like Parkinson’s disease, medications that increase dopamine levels or mimic its effects on the brain are often prescribed.
- Dietary adjustments, exercise, and stress management techniques can play a supportive role in managing dopamine deficiency.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals develop coping mechanisms and strategies to manage symptoms associated with low dopamine.
















